How can ESCO autoclave solve your troubles?
ESCO delivers reliable, efficient sterilization solutions for end-users and offers flexible, stable partnerships for distributors, driving industry standards and earning market trust through superior technology and service.
Our brands in this segment









What are the concerns of dental clinics regarding dental autoclave?
Dental autoclaves (also known as dental autoclave equipment) The pain points of dental clinics are mainly focused on equipment performance, operating experience, cost-effectiveness and regulatory compliance.
- Reliability of Sterilization Effect
- Ease of Operation and Use
- Efficiency and Equipment Stability
- Regulatory Compliance and Record Management
- Space and Cost Optimization
What concerns do dental medical product distributors have about sterilizers?
The pain points of dental autoclave distributors mainly focus on product quality, market competition, customer service, supply chain management, and profit margins.
- Product Quality and Stability
- Intense Market Competition
- Customer Education and Technical Support
- Inventory Management and Supply Chain Issues
- Limited Profit Margins
- Insufficient Brand and Market Support

Maybe it's suitable for your product
Rest assured, all of our products are accompanied by international certifications, guaranteeing the utmost standards of quality and safety.
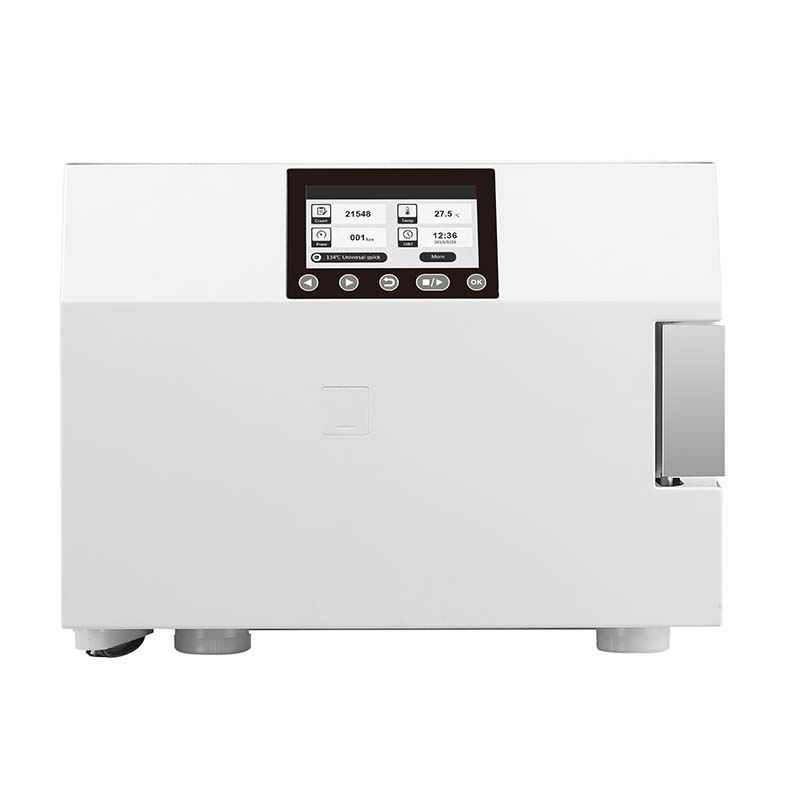
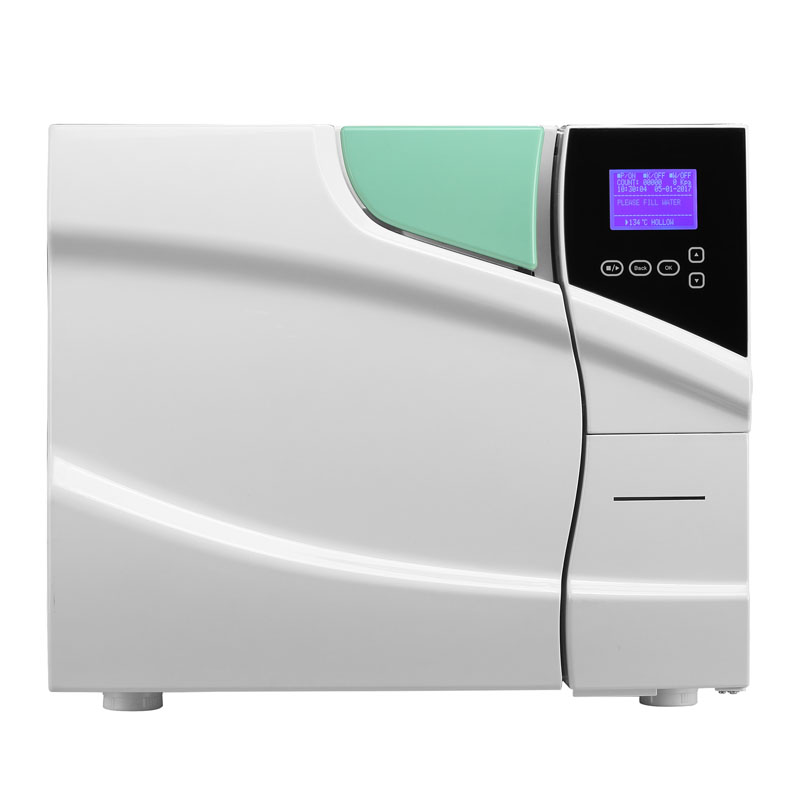
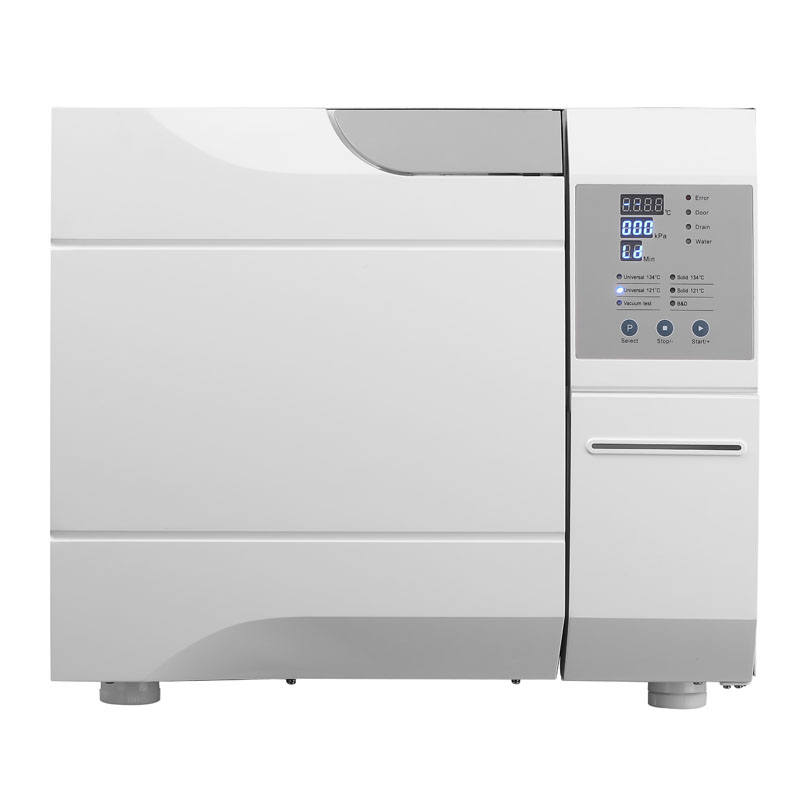
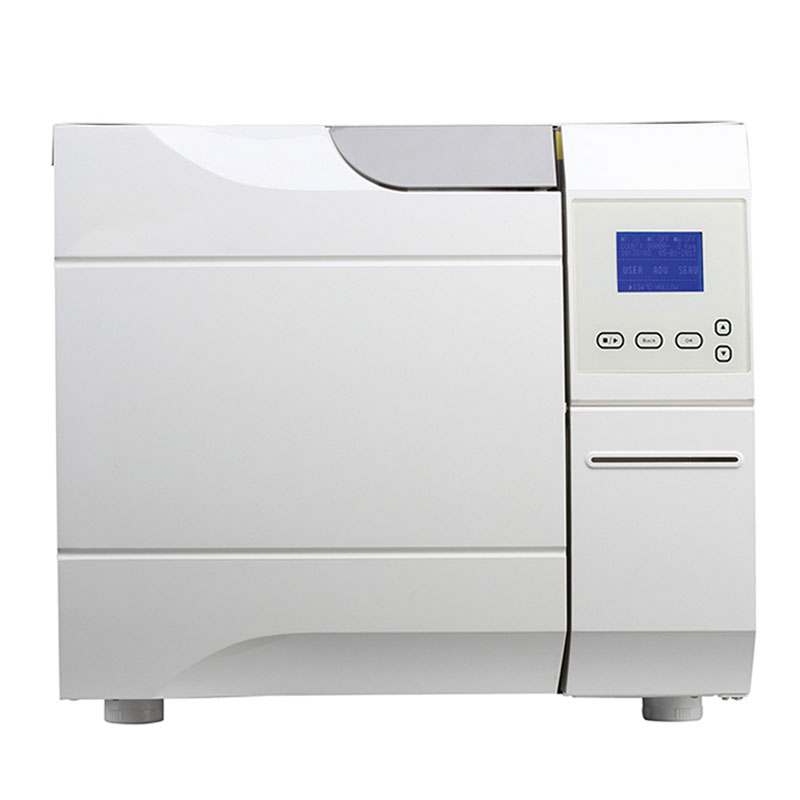
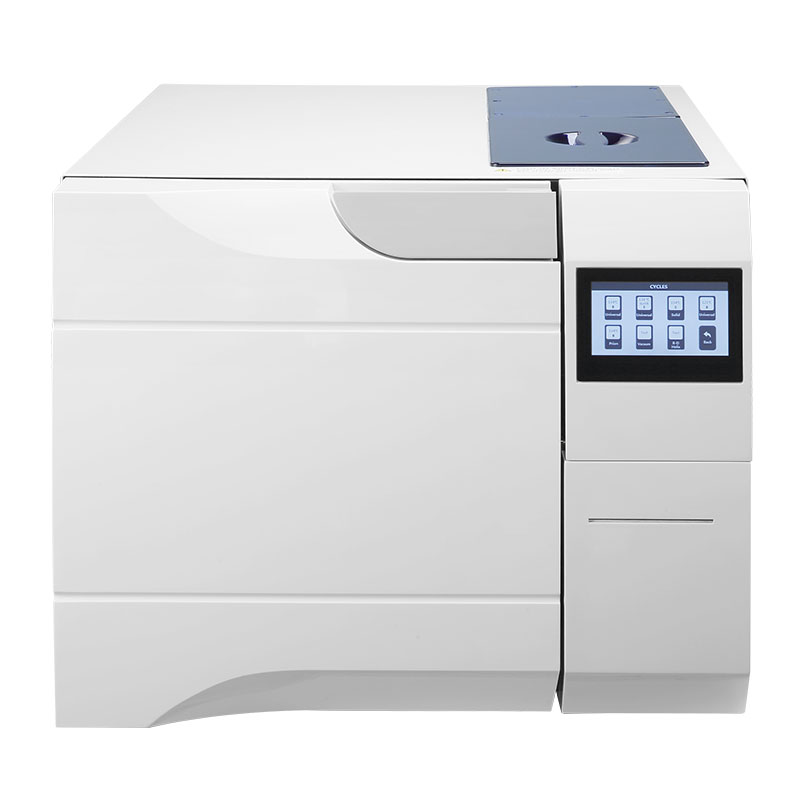
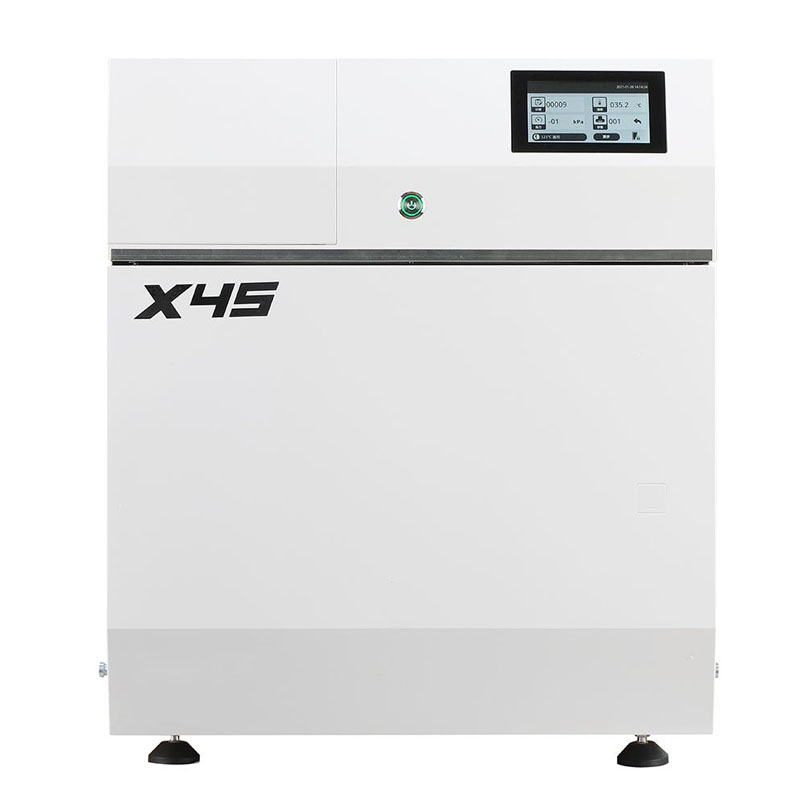








Our Best Services
Share processes an data secure lona need to know basis without the need
Our prices are clear and straight forward
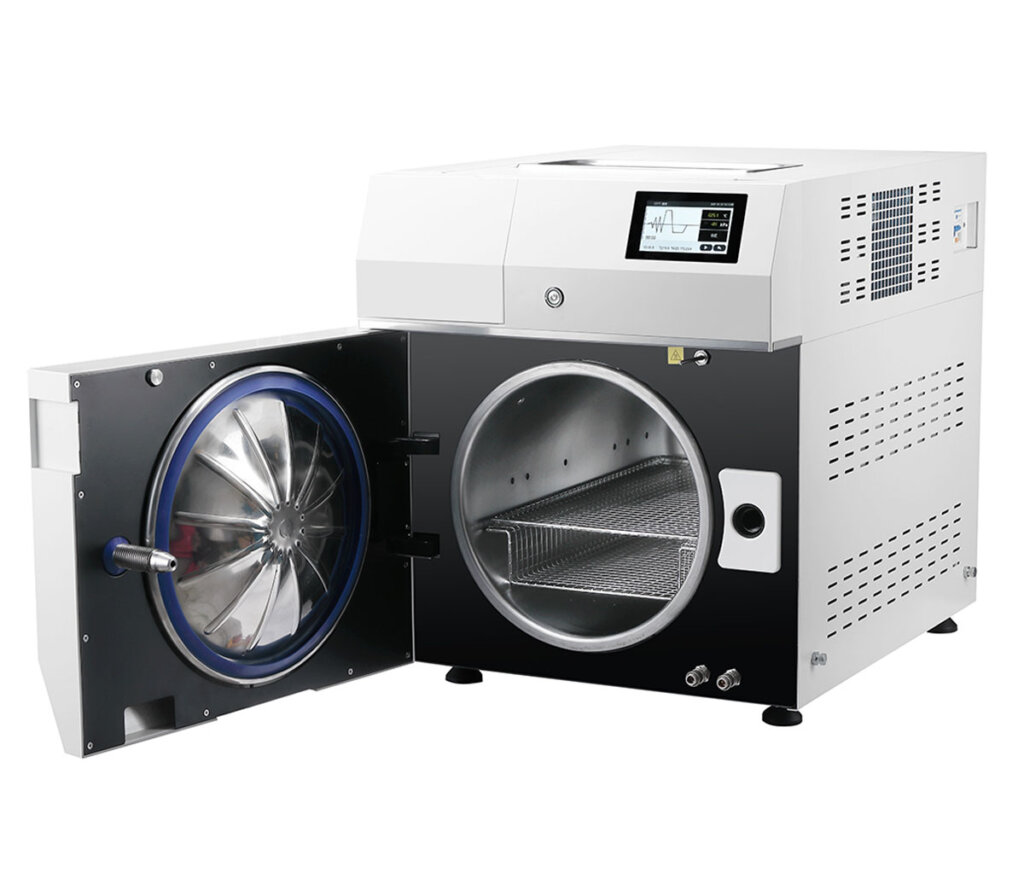

Class B Dental Autoclave
Flexible Design to Meet Diverse Needs
ESCO offers a range of capacities and models to cater to the varying demands of small dental clinics and large hospitals.
The flexible chamber and tray design accommodate a wide variety of dental instruments, including complex tools and small components, helping end-users optimize instrument processing efficiency.
Deeper Sterilization For Challenging Media
Class B autoclaves are the top standard in steam sterilization, ideal for medical, dental, and laboratory use. Their vacuum system ensures complete sterilization, even for porous or complex items, providing precision and reliability in healthcare and research settings.
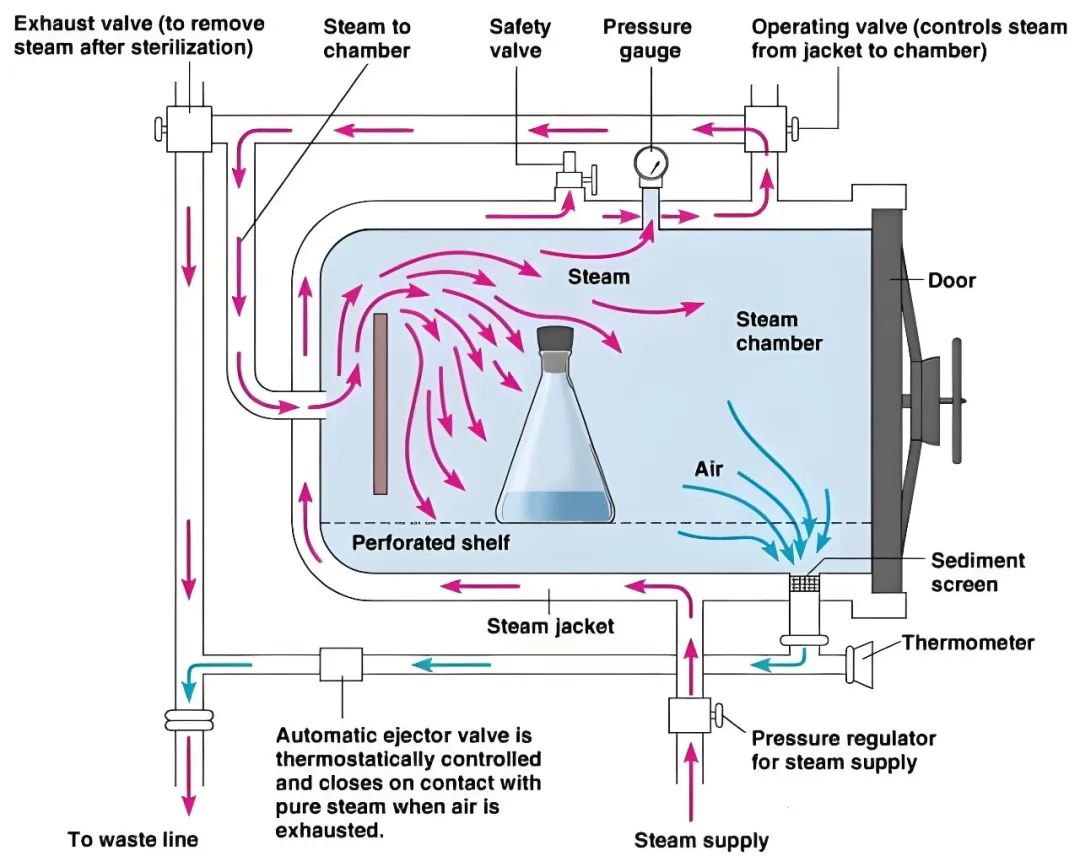

Smart Operation for Simplified Use
Equipped with a user-friendly intelligent touchscreen interface and one-touch start function, ESCO devices significantly reduce complexity, making them easy to operate even for beginners.
Multi-language interfaces and operation guides cater to diverse market needs, making it easier for distributors to promote the products to end-users.
Durable and Reliable with Low Maintenance Costs
Crafted with high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing processes, ESCO dental autoclave ensures exceptional durability and low failure rates, reducing maintenance burdens for both end-users and distributors.
With long-term warranties and professional after-sales support, we guarantee stable performance, easing the service demands on distributors.


Energy-Efficient and Environmentally Friendly, Reducing Operating Costs
Optimized energy management reduces electricity and water consumption, meeting modern environmental standards and helping users save on operating costs.
The innovative wastewater treatment system ensures pollution-free discharge, complying with strict regulatory requirements and facilitating market expansion for distributors.
Comprehensive Support for Distributor Success
We provide professional market support, including product demonstrations, promotional materials, and training services, to help distributors promote products more effectively.
We ensure stable supply cycles, support flexible inventory management, and offer favorable policies to enhance distributor operational efficiency and profit margins.

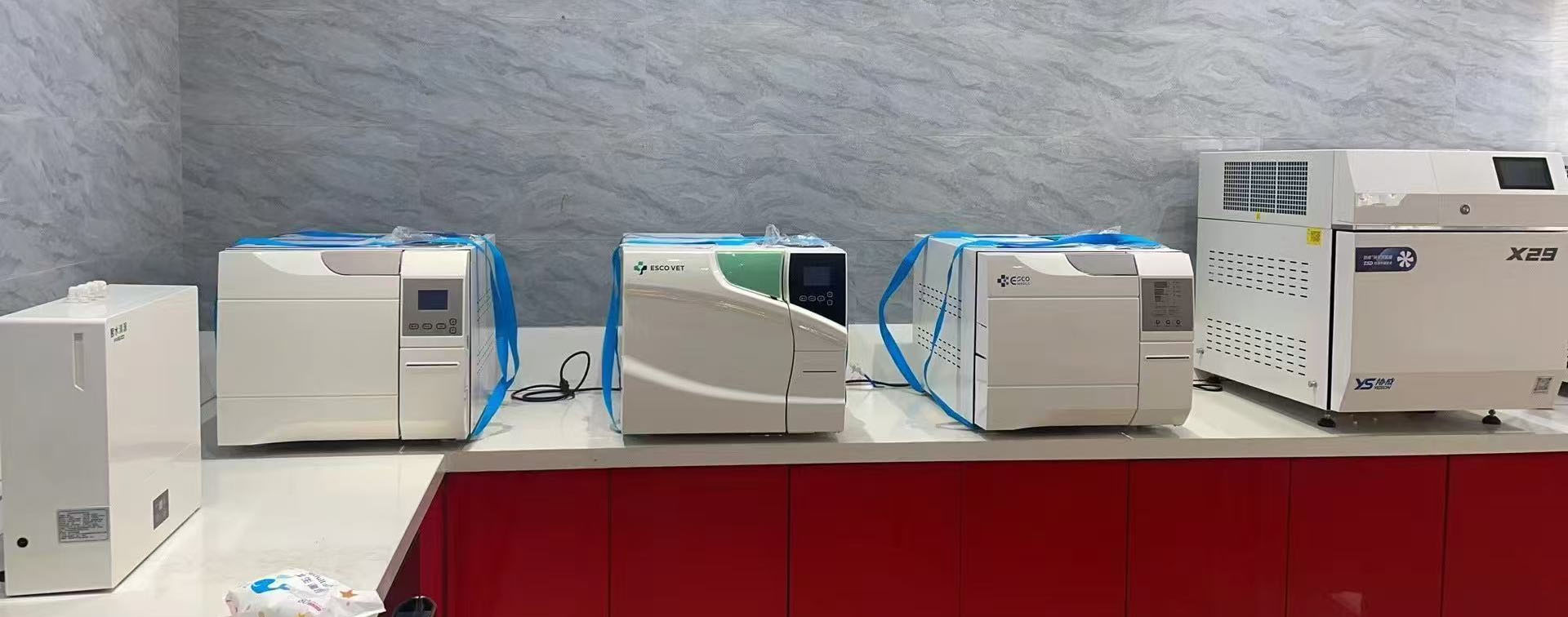
Physical display
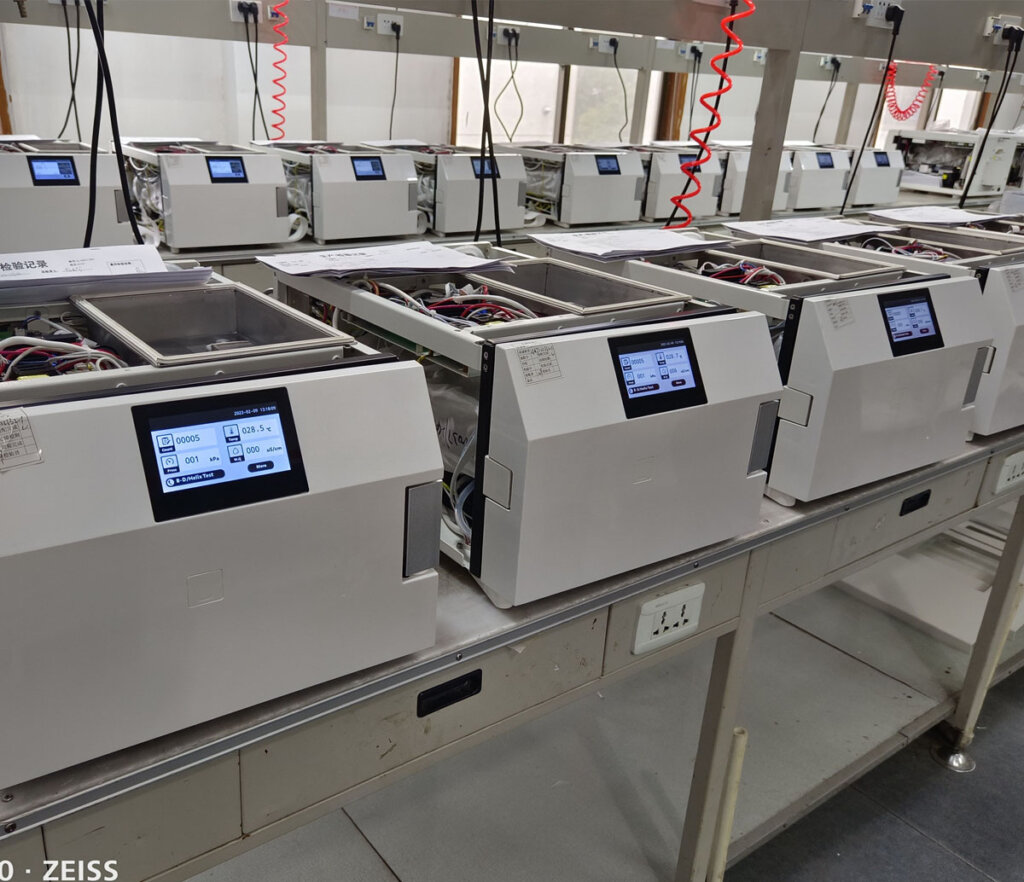
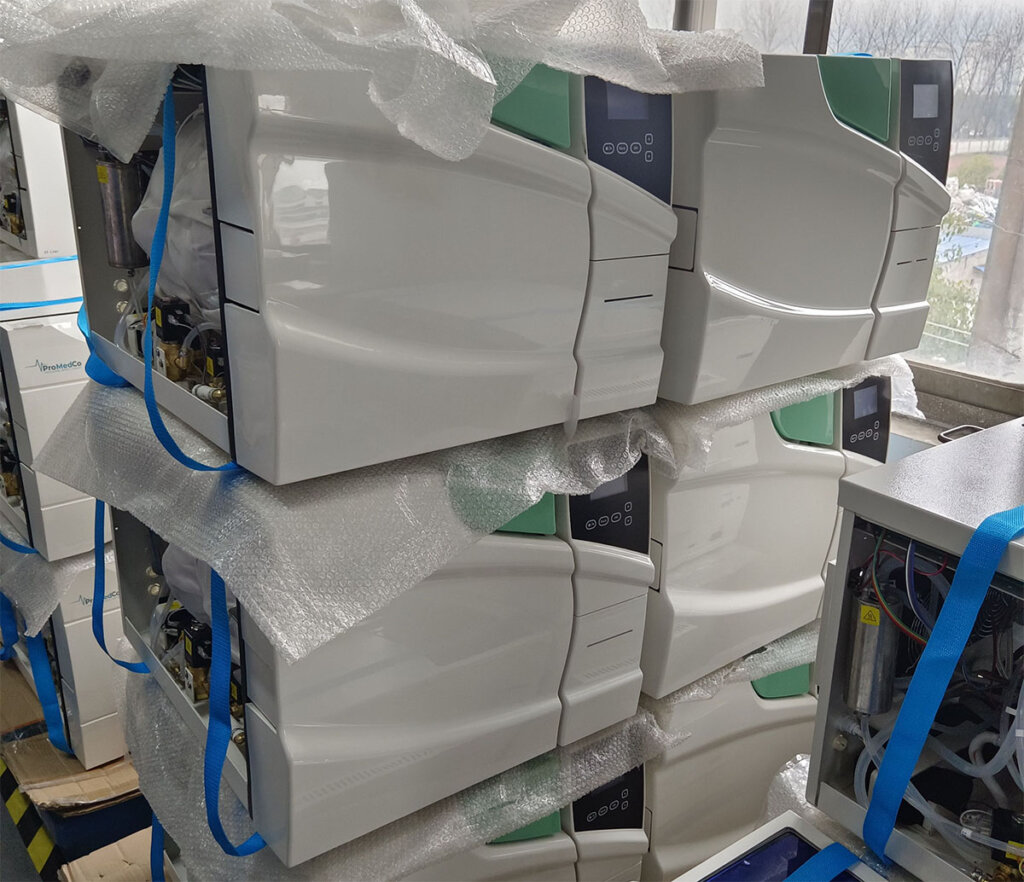
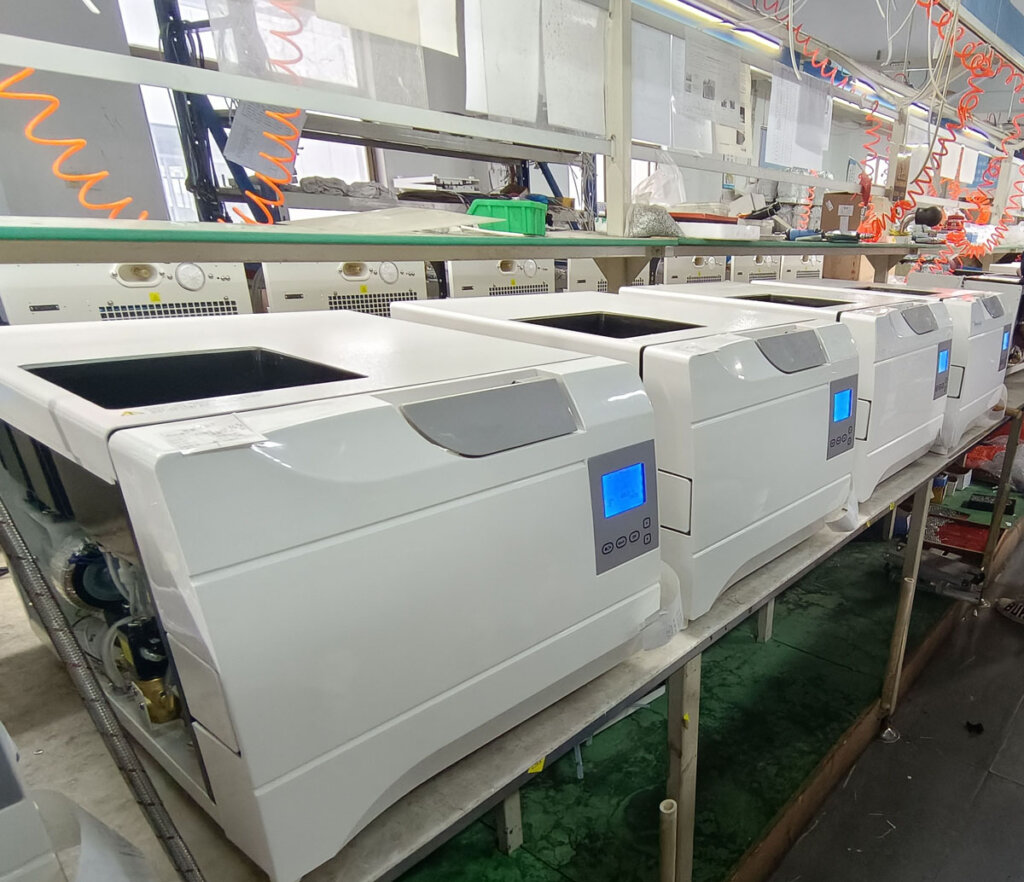




What else do you want to know?
We will sincerely provide you with the most competitive prices and solutions.
While autoclaves solely utilize steam to disinfect, sterilizers can use chemicals, high pressure, filtration, irritation, or a combination of these methods to eliminate living organisms.
Autoclaves are used in education, research, biomedical research, pharmaceutical research and industrial settings to sterilize lab instruments and glassware, process waste loads prior to disposal, prepare culture media and liquid media, and artificially age materials for testing.
The autoclaving process takes advantage of the phenomenon that the boiling point of water (or steam) increases when it is under high pressure. It is performed in a machine known as the Autoclave where high pressure is applied with a recommended temperature of 250°F (121°C) for 15-20 minutes to sterilize the equipment.
- Acids.
- Explosive Material.
- Flammable Material.
- Chlorine Based (or chlorine included) Products.
- Reactive, Corrosive, or Toxic Materials.
- Radioactive Material.
Boiling Water
Boiling inactivates bacteria, protozoa, viruses and other pathogens by using heat to damage them structurally. You can use this for Niobium, Titanium, stainless steel, Pyrex glass, quartz glass and bioplastic. Keep acrylic jewelry away from hot water and use other sterilization
Checkout How ESCO Autoclaves Fit Into Your Application
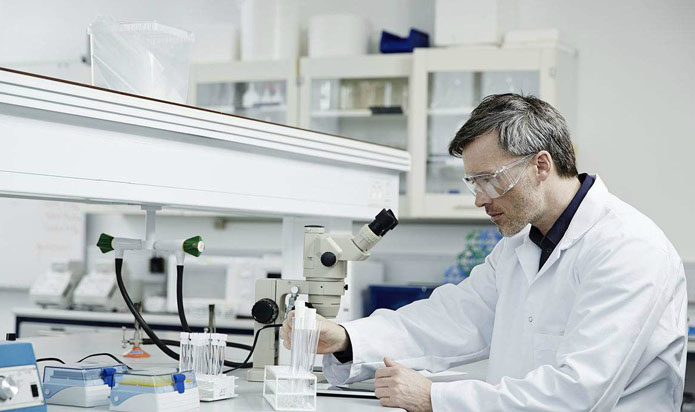

Laboratory
See why autoclaves are essential in academic and university research laboratories.
About Us

1.
Offering comprehensive dental equipment supply
We prioritize reliable, well-established equipment and tailored solutions. Our account managers provide you with professional advice on products, technology, daily operations, and sales practices.
2.
Exclusive regional distribution and authorization
Exclusive agreements ensure compliance, with region-specific rules and differentiated pricing. Distributors get priority for new launches, trademark protection, and marketing support, along with after-sales service and free training.
3.
Providing comprehensive technical service and support
ESCO provide you with comprehensive support from pre-sale to after-sale through manuals, remote guidance and on-site service.
About Us
Advantages of Partnering with ESCO
-
Established Network and Customer Base:Quickly reach target customers and enhance brand credibility.
-
Understanding of Market Trends and Regulations:Ensure product compliance, adapt to market changes, and reduce risks.
-
Streamlined Logistics and Supply Chain:Improve delivery efficiency, lower costs, and ensure reliable supply.
-
In-depth Knowledge of Local Markets:Customize products to meet demand, boosting competitiveness and satisfaction.
-
Accelerated Market Penetration:Enter markets faster, expand brand reach, and drive sales growth.
-
Increased Sales and Satisfaction:Achieve higher revenue and customer loyalty, fostering business growth.
Since 2010
20
years of experience in dental medical equipment industry

Sterilization Auxiliary Product

One-stop supply/Localregistration/Factory price/Worry-freewarranty
JOIN US
Medical high-tech enterprises are recruiting global agents
How Can We Help?
START YOUR DENTAL MEDICAL PRODUCTS ONE-STOP PURCHASING JOURNEY
We'd like to work with you
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. Our experts will give you a reply within 24 hours and help you choose the right product solution
- What'sApp: +86 18344685960
- Email: sales@escomedical.com.cn
- Add: NO.188, West Shihu Road Wuzhong, Suzhou China