Chapter 1
What Are Dental X Ray Machine?
In modern dental practice, X-ray machines are an essential tool that aids dentists in making accurate diagnoses and providing effective treatments. Different types of dental X-ray machines have their own advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial to fully understand these aspects when selecting the right equipment. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the most common types of dental X-ray machines available on the market, helping dentists and clinic managers make informed decisions to ensure they choose the equipment that best suits their specific needs.
Request A Free Quote
Connect with us to begin. Explore the top-selling dental medical equipment for your market’s needs. Use the contact form below or call us today. Your smart future awaits.
Reply within 24 Hours
Please complete the form below and our customer support team will be in touch with you shortly. Inquiries submitted through this form will receive priority processing over emails.
- Email: sales@escomedical.com.cn
- What'sApp: +86 18344685960
- Add: NO.188, West Shihu Road Wuzhong, Suzhou China
Chapter 2
Types of dental x ray machine and their functions
Dental X-ray machines are generally classified into the following types:
Traditional X-ray Machine
This is the most common type, which records images on film. While it provides high-quality imaging, it is more complex to operate and requires a certain amount of time to capture the image.Digital X-ray Machine
Compared to traditional X-ray machines, digital X-rays provide clearer and faster images. The images can also be processed and stored via a computer, enhancing overall efficiency.Panoramic X-ray Machine
This device captures an image of the entire oral cavity in one shot, allowing doctors to gain a comprehensive view of the patient’s oral health.CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography)
This advanced imaging technology provides three-dimensional images, assisting doctors in making more precise diagnoses.Portable X-ray Machine
These machines are easy to operate and generally simple to use, making them suitable for dental assistants or nurses. They are highly flexible and can be used in various locations, making them ideal for mobile clinics or on-site services.

Chapter 3
The basic working principle of dental X-ray machine
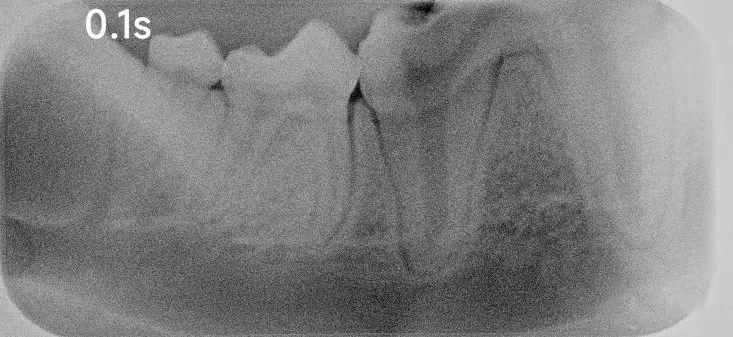
The core principle of a dental X-ray machine is based on the varying absorption levels of X-rays as they pass through objects, in this case, the patient’s oral cavity. Different densities within the oral structures result in different levels of X-ray absorption. Denser areas, such as teeth, absorb more X-rays, while less dense areas, like soft tissues, absorb fewer X-rays. These variations in absorption form an image that dentists can analyze.
In practice, the dentist positions the X-ray machine to target the patient’s oral cavity and quickly emits X-rays. The resulting images are displayed on a screen, allowing the dentist to observe the condition of the teeth, gum health, and bone structure. This quick and non-invasive examination method significantly enhances diagnostic efficiency.
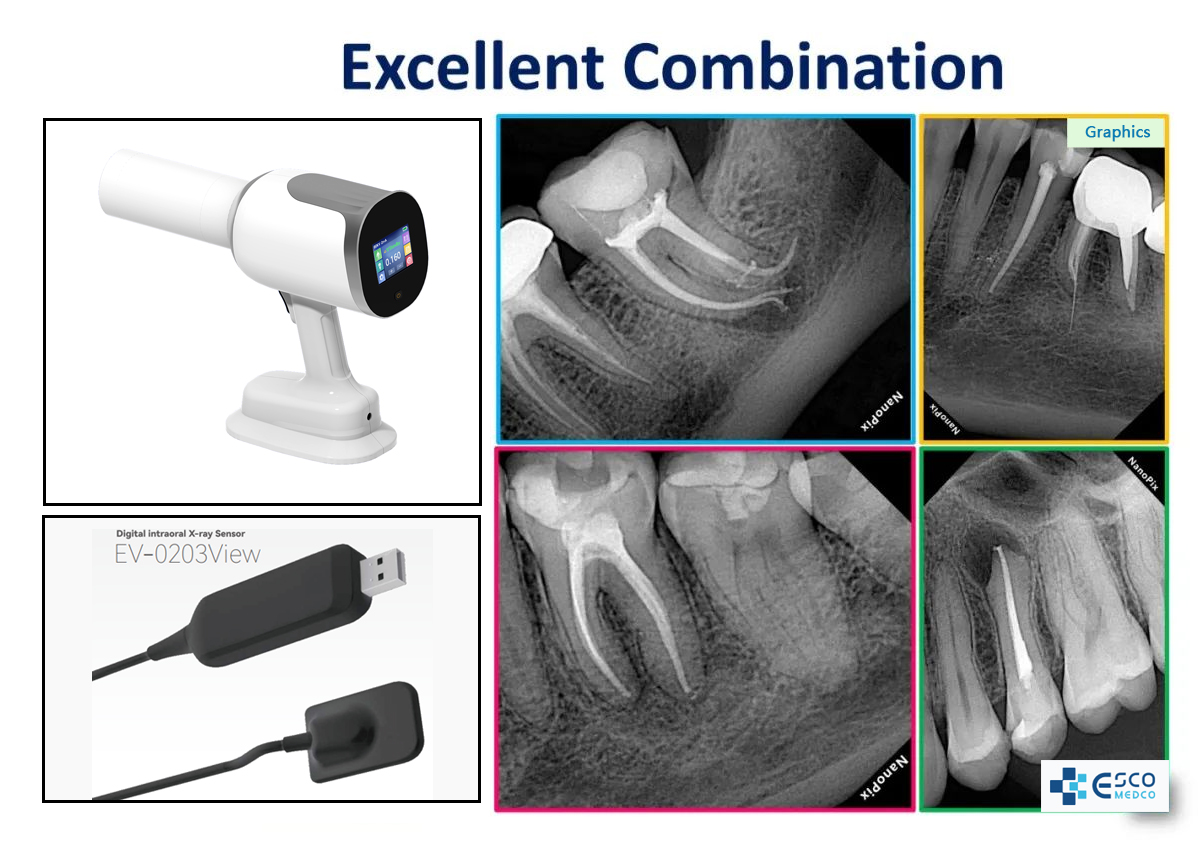
Chapter 4
Application field of dental X-ray machine
Cavity Detection:
Dental X-ray machines assist dentists in identifying early-stage cavities, especially in areas that are difficult to observe with the naked eye, such as the occlusal surfaces and between teeth.Root Canal Treatment:
During root canal procedures, dentists require clear images to determine the shape of the root canals and the extent of infection. Dental X-rays provide essential support in this process.Dental Alignment Analysis:
For patients requiring orthodontic treatment, X-ray imaging offers detailed information on tooth alignment, aiding dentists in creating effective treatment plans.Tooth Extraction:
When extracting wisdom teeth or other teeth, X-ray images help dentists understand the structure of the tooth roots, reducing the risk of damaging surrounding tissues.Oral Disease Diagnosis:
Many oral diseases, such as periodontal disease and cysts, can be detected early through X-ray examinations, enabling timely treatment.
Chapter 5
Understand the key parameters of dental X-rays
Dental X-ray machines on the market vary widely in appearance and price, and the promotional claims from different sellers can sometimes be confusing. Without knowing how to evaluate them, you might end up paying a high price without getting a high-performance product. The performance of these machines lies hidden in their specifications. To effectively evaluate a dental X-ray machine, it’s essential to understand and analyze several key parameters comprehensively. These include the high-voltage generator frequency, focal spot size, tube voltage, tube current, focal spot-to-skin distance, exposure time, and total filtration.
Focal point
What is a focal spot? The focal spot is the area on the target of an X-ray tube where electrons collide. Its unit is millimeters (mm), referring to the nominal value of the effective focal spot size, not its actual length or width.
The smaller the focal spot, the sharper the image edges. While a small focal spot provides higher image clarity, it reduces the efficiency of X-ray production and limits heat dissipation. Therefore, tiny focal spots are typically used to produce a limited amount of X-rays, suitable for applications such as dental imaging, cardiovascular fluoroscopy, and small animal
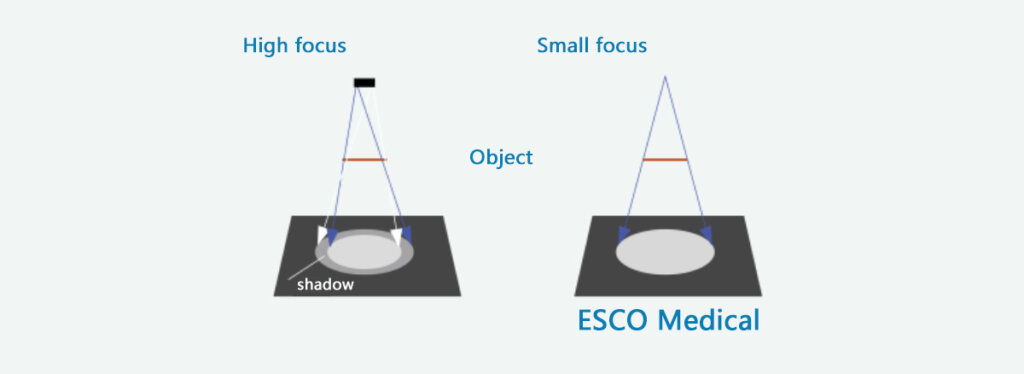
The focal spot of dental X-ray machines is typically a single spot, ranging from 0.3mm to 1.5mm. Mainstream dental X-ray machines generally achieve a focal spot size as small as 0.4mm. A 0.4mm focal spot offers slightly higher image sharpness. With a 0.8mm focal spot, due to the lower tube voltage and slightly higher milliampere-seconds (mAs), The generated image has relatively low clarity.
Focal skin distance
The shortest distance from the X-ray tube focal spot to the patient’s skin is called the focal spot-to-skin distance (FSD). As shown in the diagram, the FSD is the distance from the focal spot marked on the X-ray tube to the front end of the collimator. In the illustrated example, FSD = the length of the collimator + the distance from the tube focal spot to the collimator interface. The longer the collimator, the greater the FSD. Some machines are equipped with two collimators, while others have only one.
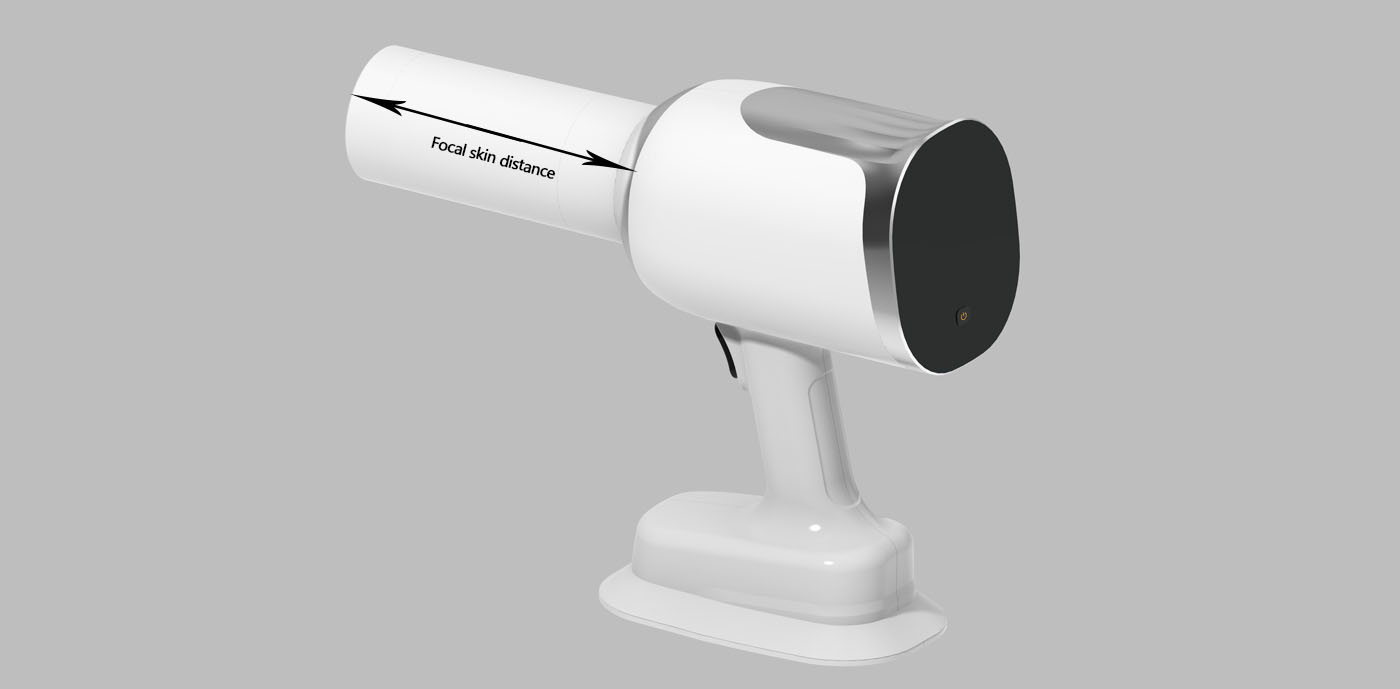

Radiation Divergence
With a larger focal spot-to-skin distance (FSD), the X-ray beam divergence is reduced. In other words, the greater the FSD, the more focused the X-ray beam becomes.
To prevent patients from unnecessary radiation exposure during dental X-ray imaging, standards require that the focal spot-to-skin distance (FSD) for dental X-ray machines must be at least 200mm.
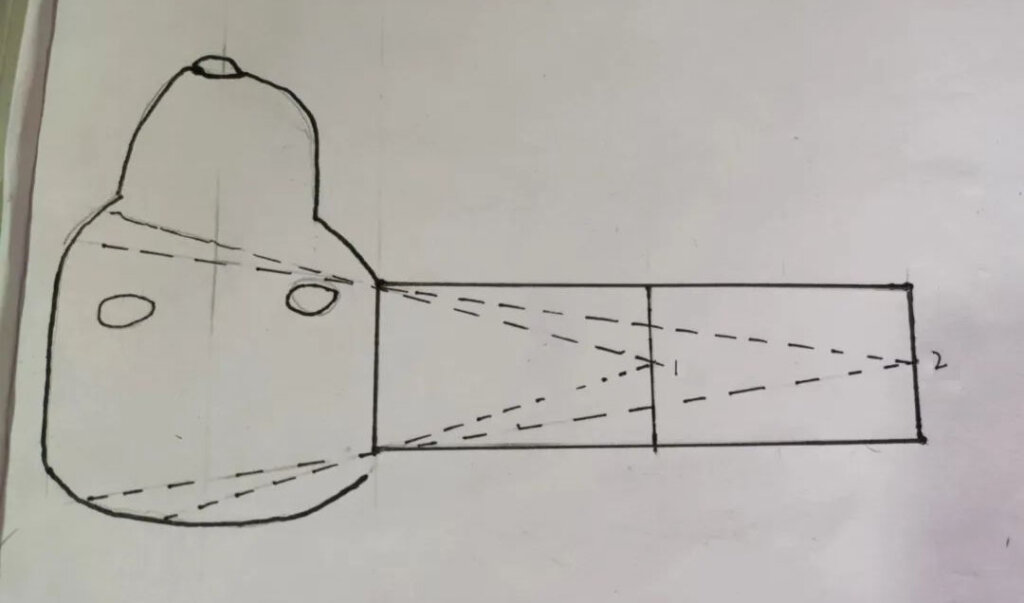

Image Length Distortion
When an X-ray detector is placed at a specific position, the image produced by a focal spot that is further away will appear smaller and less magnified. Therefore, X-ray machines with a larger focal spot-to-skin distance (FSD) produce images with lengths that are closer to the actual size.
When selecting a veterinary dental X-ray machine, a focal spot-to-skin distance of 200mm is preferable. A larger FSD reduces radiation scatter and minimizes image distortion, ensuring the image length is more accurate. Although a larger FSD requires a threefold increase in exposure time, modern high-frequency dental X-ray machines equipped with DR detectors can achieve exposure with very short times, making this adjustment less of an issue.
Tube current
Understanding Milliampere (mA) and Tube Current
Milliampere (mA) is the unit of tube current. Tube current refers to the amount of current passing through the cathode filament in the X-ray tube.
The cathode filament is heated by electric current, releasing electrons. These electrons are accelerated by high voltage and strike the anode target. The focal spot on the target, where the electrons hit, generates X-rays. The electrons are produced by the cathode filament’s heating, and the tube current (measured in milliamperes, mA) determines the efficiency of electron production. Therefore, the size of the tube current determines the density of X-rays generated by the X-ray tube within a given time. A higher mA results in a greater X-ray density produced per second, leading to more pronounced film blackening.
The Impact of Exposure Time on Film Blackening
The longer the exposure time, the more pronounced the blackening of the X-ray film. Therefore, the product of milliampere (mA) and seconds (s), known as mA·s, determines the total amount of X-rays emitted during an exposure. This, in turn, indirectly determines the degree of film blackening.

What is the impact of tube current on X-ray imaging? Tube current primarily affects two factors: the exposure time and the thickness of the tissue being imaged.
Exposure Time: Under the same conditions, the higher the tube current, the shorter the required exposure time. With a constant milliampere (mA) value, the longer the exposure time, the greater the X-ray density emitted by the tube. Therefore, the product of mA and exposure time (mA·s) determines the X-ray density emitted by the tube. For example, to generate 10 mA·s of X-rays, if the tube current is 10 mA, the exposure time would need to last for 1 second. However, if the tube current is reduced to 1 mA, the exposure time would need to be 10 seconds. As the tube current increases, the required exposure time decreases. In essence, a higher tube current makes the exposure more efficient. If the tube current is increased by 100 times, the exposure time is reduced to 1% of its original value.
Tissue Thickness: With a constant kVp (kilovolt peak), an X-ray machine with a higher mA can handle thicker tissues during imaging.
In summary, under the same conditions, the higher the tube current (mA), the better the performance of the machine.
Chapter 6
Choose a good dental X-ray machine for you
Digital imaging in dentistry is becoming increasingly popular, and taking X-ray films has almost become a necessary part of dental checkups. It is crucial to choose a dental X-ray machine that offers high image quality, fast exposure times, and ensures patient safety.
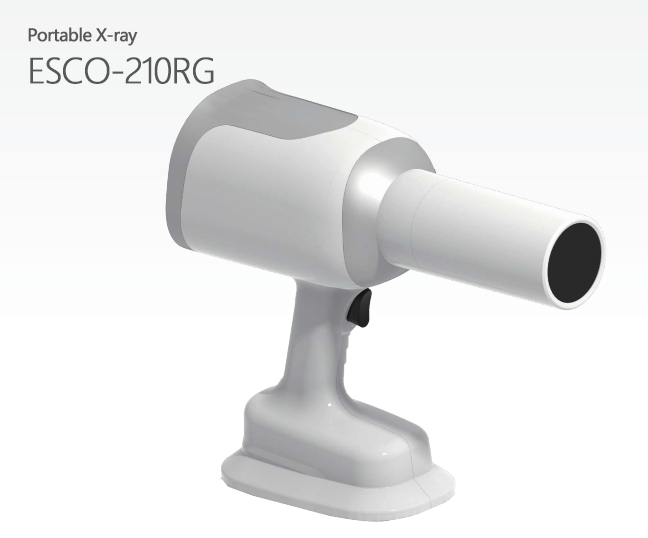

Portable X-ray
ESCO-210R
Ray Imaging ESCO-210RG dental X-ray machine is a portable device designed for single-person operation. Its simple design and flexibility allow dentists to easily adjust imaging angles and cap ture X-ray images efficiently. This user-friendly device is ideal for quick and flexible dental imaging needs.

Portable X-ray machine

Digital flat panel detector
Lead glass

Occlusal scaffold
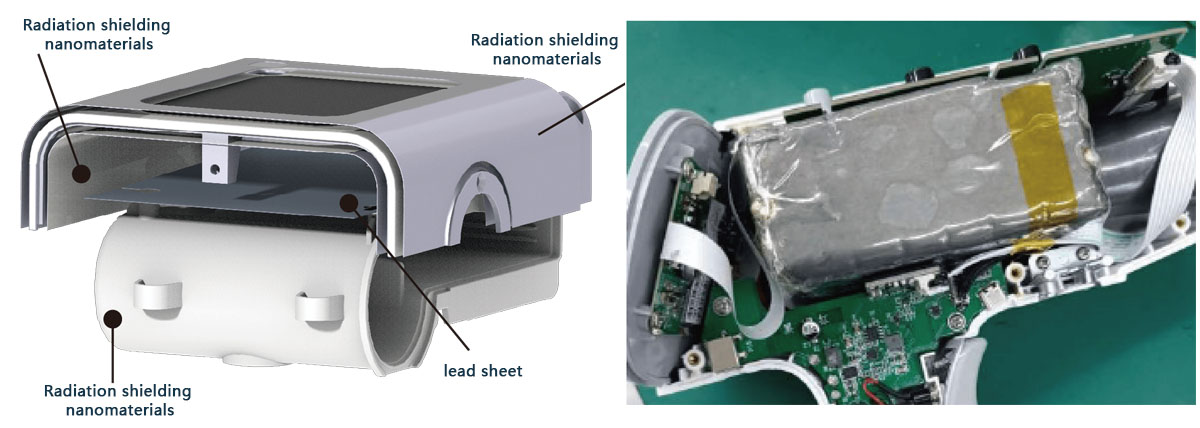
Ultra-low radiation, 30% less exposure
5-layer nano radiation protection and leakage control technology. The radiation exposure in the compartment is 0,
providing the highest level of protection for medical staff.
Ultra-low radiation, only 0.0007mGy/H, the exposure dose is reduced by more than 30% compared with the standard generator, maximizing the effective rays and reducing the radiation intensity.
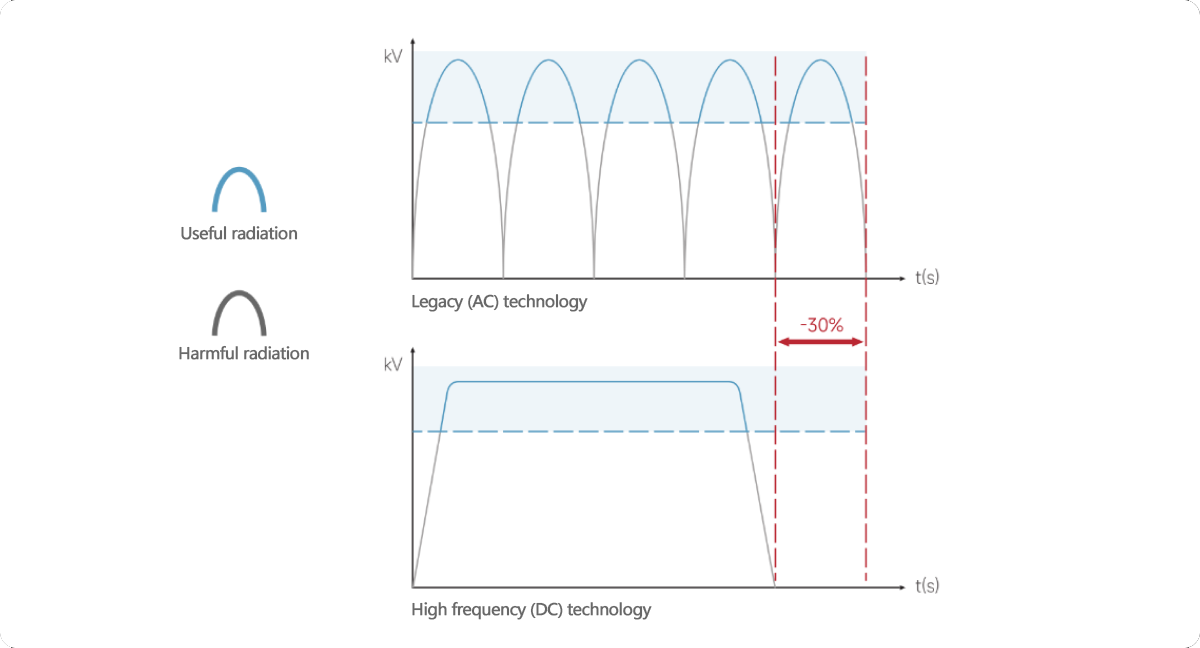
High image quality
500kHz ultra-high frequency inverter technology based on Silicon Carbide (SiC) MOSFETs.
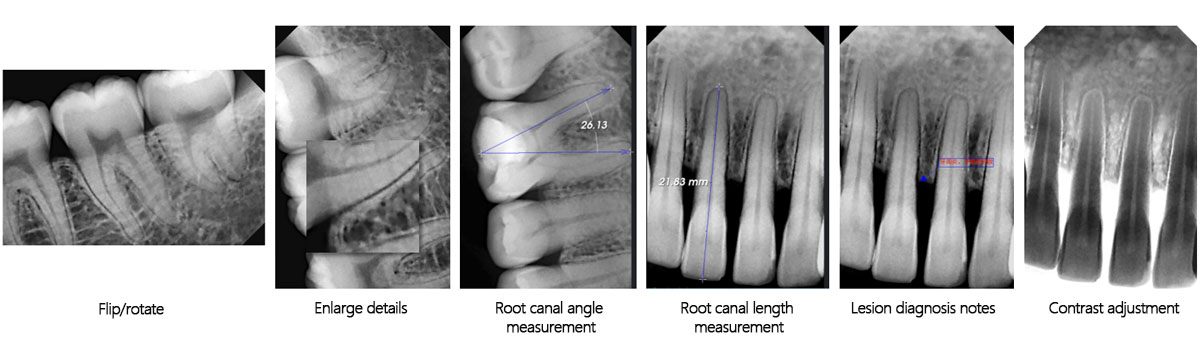
Image clarity is enhanced by 50%, enabling precise visualization of hidden lesions.
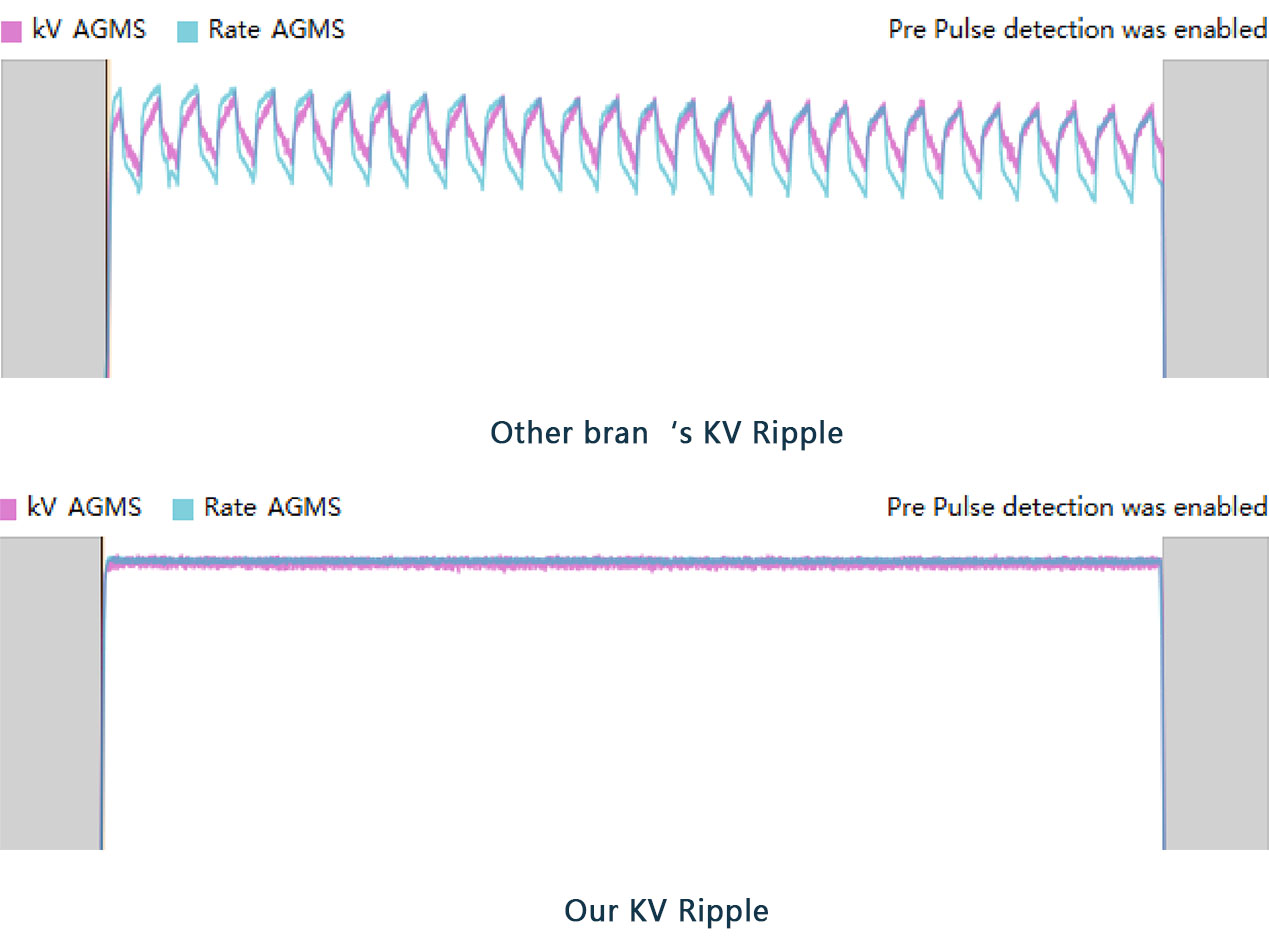
Ultrafast imaging in 0.01 seconds delivers high-resolution images that capture every detail and help dentists make more accurate diagnoses.
| ESCO core parameters | ||
| Focal point | 0.4 | Microfocus with less shadow Sharp and clear image |
| Tube current | 2.5mA | .Higher tube current than similar products .Short exposure time .Effective anti-shake. .Low radiation |
| Tube voltage | 60kV to 70kV | More penetrating |
Works With All Dental Films
Open-ended consumables, compatible with sensors from major brands, phosphor plates (such as DentalX), and traditional films.

Long battery life
Equipped with high-capacity carbon-core lithium battery, it can take 200 dental films under full charge, and the fastest charge is 20 minutes.

Intimate design
Designed for single-user operation, weighing only 2.2kg, making it a lightweight option in the domestic market. It can be held with one hand during exposure, reducing the risk of hand tremors and ensuring high image quality.

What Can ESCO Bring to Dentists?
Let Your Imagination Run Wild
Go Beyond
What else do you want to know?
We will sincerely provide you with the most competitive prices and solutions.
Dentists use computed tomography (CT) scans to capture 3D dental X-rays of your teeth, jaws, joints, nerves and sinuses. These X-rays can also detect tumors or facial fractures. Surgeons often use dental CT scans to check the height, width and location of your jawbone before dental implant placement.
There are two main types of dental X-rays: intraoral (the x-ray film is inside the mouth) and extraoral (the x-ray film is outside the mouth). Intraoral x-rays are the most common type of X-ray.
Stand behind a shield or at least six feet from the X-‐ray source, and out of the path of the primary beam. Give warning before pressing exposure button to protect co-‐workers and patients. Never hold a receptor for a patient.
Yes, children can receive dental X-rays when appropriate, but it is important to carefully control the radiation exposure.
Digital X-ray machines capture images quickly, offer easier processing, and provide higher image quality, while traditional X-ray machines require film processing, which takes longer.
The price of dental X-ray machines varies depending on the brand and type, generally ranging from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
Client Testimoninals
One-Stop Dental Equipmentleading Brand
It has been a pleasure working with you and your team. Your company has played a crucial role in our ability to meet and exceed our clients' expectations. I am truly grateful for everything you and your team have done, and I look forward to continuing our partnership as we both grow and evolve in the future.
Shams W.Pawel Dental medical equipment dealer customersWhat are you waiting for?
Connect with us to begin. Explore the top-selling dental medical equipment for your market’s needs. Use the contact form below or call us today. Your smart future awaits.
Reply within 24 Hours
Please complete the form below and our customer support team will be in touch with you shortly. Inquiries submitted through this form will receive priority processing over emails.
- Email: sales@escomedical.com.cn
- What'sApp: +86 18344685960
- Add: NO.188, West Shihu Road Wuzhong, Suzhou China



